Key Takeaways
- PCPs offer consistent, non-pulsating flow, making them suitable for handling complex fluids.
- Due to their versatility and efficiency, they excel in industries such as wastewater treatment, oil and gas, and food processing.
- Advancements in PCP technology have led to improved durability, reduced maintenance, and enhanced energy efficiency.
Progressive cavity pumps (PCPs) have cemented their status as pivotal assets in industries where precision and reliability in fluid movement are essential. Known for their unique ability to maintain consistent flow, these pumps tackle the challenges of transferring viscous, abrasive, and shear-sensitive materials—a feature indispensable in sectors from wastewater management to food production. Many facilities have turned to https://cbeuptime.com/roper-pumps/ for their progressive cavity pump needs, leveraging the advanced designs available to optimize operational efficiency and minimize unplanned downtime. Their robust design and precise handling capabilities set PCPs apart from more conventional pumps. Whether the requirement is the gentle movement of dairy products or the aggressive transfer of oil-laden slurries, progressive cavity pumps deliver reliability that supports productivity and cost control. Their role in modern fluid handling exemplifies how engineering innovation continues to reshape industrial workflows.
Understanding Progressive Cavity Pumps
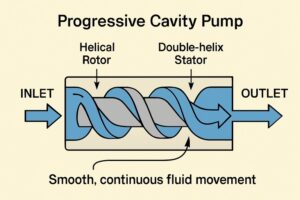
The distinctive mechanism within a progressive cavity pump comprises a single helical rotor turning inside a double-helix stator. This pairing forms discrete, tightly sealed cavities, which progress steadily from the suction to discharge ends as the rotor rotates. As a result, fluid is carried smoothly, avoiding the pulsing or surging often seen with reciprocating or peristaltic pumps. Because of this steady movement, PCPs can handle diverse fluid types—from free-flowing chemicals to highly viscous sludge—without compromising system efficiency or risking product degradation.
The engineering behind PCPs enables them to generate significant suction and discharge pressures, while their gentle conveyance preserves the integrity of sensitive mixtures. This is especially critical in industries where product quality or process consistency is paramount, and where abrasive media might otherwise shorten the lifespan of less rugged pump types.
Applications Across Industries
PCPs have proven their worth in diverse industrial environments, particularly where routine operations involve challenging or variable fluids. In wastewater treatment plants, PCPs are the backbone of sludge and slurry management, as their ability to maintain even flow rates ensures process stability. At the same time, the gentle action is advantageous for biological processing. The oil and gas sector has embraced this technology, notably in hydraulic fracturing and crude transfer. Here, progressive cavity pumps deliver fluids efficiently despite high pressures, abrasive content, and fluctuating material characteristics. Recent advances have further enhanced their suitability, as highlighted by numerous industry reports showing longer pump lifespans and faster ROI. Progressive cavity pumps play a vital role in preserving the quality of sensitive products such as dairy, sauces, and juices in food and beverage manufacturing. Their non-pulsing, gentle movement prevents separation, foaming, or textural changes, making them indispensable wherever throughput consistency and stringent hygiene standards are enforced.
Advantages of Progressive Cavity Pumps
- Handling High Viscosity and Abrasive Fluids: The rotor and stator configuration is highly resilient, making it possible to transfer thick, abrasive media with less wear and tear than traditional pump types. This dramatically reduces both maintenance frequency and part replacement costs.
- Non-Pulsating Flow: The smooth, continuous fluid transport supports precise dosing, metering, and blending operations. This stability safeguards process equipment and final product integrity in processes sensitive to pressure fluctuations.
- Self-Priming Capabilities: PCPs naturally expel air and can establish a prime even when suction lines contain gas pockets, simplifying start-up in tricky installations and mitigating the risk of dry-running damage.
These features are directly linked to higher operational uptime and improved system-wide efficiency, providing a clear advantage for process engineers and maintenance managers seeking to optimize their facilities.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency
The last decade has seen notable innovations in PCP design and operation. Adjustable stators and hardened rotors have emerged, dramatically extending the runtime between service intervals and lowering ownership costs. New models allow quicker component swaps and streamlined preventive maintenance, reducing system downtime. Energy efficiency has also taken center stage. The integration of variable speed drives gives users fine-tuned control over pump output, aligning energy input with real-time process demand. This reduces electrical consumption and stabilizes system performance, enhancing return on investment. Furthermore, modular construction has simplified both daily operations and long-term care. Improved sealing mechanisms and quick-release couplings enable technicians to resolve issues rapidly, bolstering reliability and lowering the costs tied to extended shutdowns.
Considerations for Optimal Performance
Extracting full value from progressive cavity pumps depends on several critical best practices:
- Proper Sizing: Match pump capacity and pressure ratings to the intended application for maximum efficiency and extended lifespan. Oversized or undersized models can accelerate wear or result in chronic process inefficiencies.
- Material Selection: Choosing rotor and stator materials compatible with the process media is vital for minimizing abrasion, corrosion, and chemical attack.
- Regular Maintenance: Instituting a structured maintenance schedule offers the best protection against sudden failures and premature wear, ensuring predictable performance over time.
Consulting with reputable suppliers supports decision-making and ensures pump configurations match site-specific conditions, further extending equipment reliability and cost efficiency.
Conclusion
Progressive cavity pumps play an essential role in reliable, efficient, and precise fluid handling solutions across industries. Their unique engineering supports exceptional handling of complex, variable, or sensitive process fluids, while continuous advancements in design and materials keep downtime and costs under control. For those seeking to maximize the return on their fluid transfer systems without sacrificing process integrity, PCPs are a proven investment, aligning with the modern industry’s continual drive for performance, sustainability, and bottom-line value.